GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
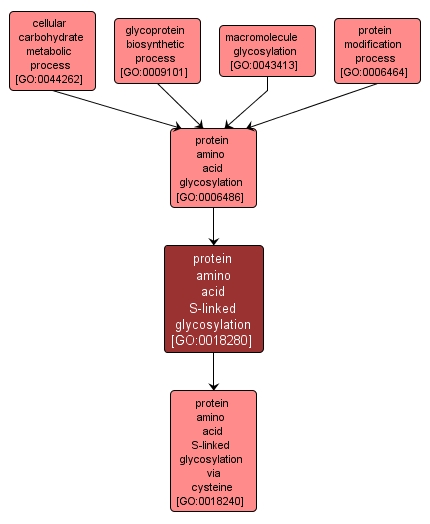
protein amino acid S-linked glycosylation |
| Acc: |
GO:0018280 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
A protein amino acid glycosylation process in which a sugar unit is added to a protein via a sulfur atom of a peptidyl-amino-acid such as cysteine or methionine. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|