GO TERM SUMMARY
|
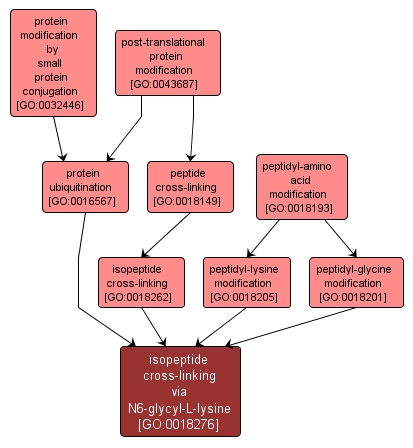
| Name: |
isopeptide cross-linking via N6-glycyl-L-lysine |
| Acc: |
GO:0018276 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The formation of an isopeptide cross-link between peptidyl-lysine and peptidyl-glycine to produce N6-glycyl-L-lysine. This is distinct from the formation of the thiolester intermediate, which occurs during ubiquitination. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|