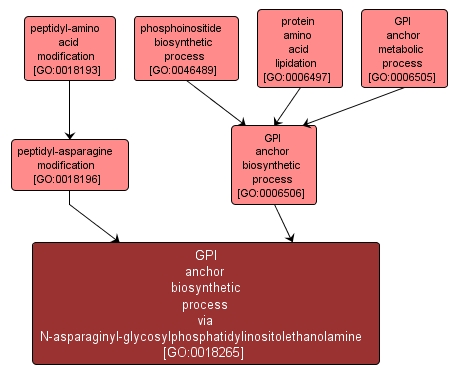
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
GPI anchor biosynthetic process via N-asparaginyl-glycosylphosphatidylinositolethanolamine |
| Acc: |
GO:0018265 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a C-terminal peptidyl-asparagine ethanolamide-linked glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor following hydrolysis of a asparaginyl-peptide bond in the carboxy-terminal region of a membrane-associated protein. |
Synonyms:
- GPI anchor formation via N-asparaginyl-glycosylphosphatidylinositolethanolamine
- GPI anchor anabolism via N-asparaginyl-glycosylphosphatidylinositolethanolamine
- GPI anchor synthesis via N-asparaginyl-glycosylphosphatidylinositolethanolamine
|