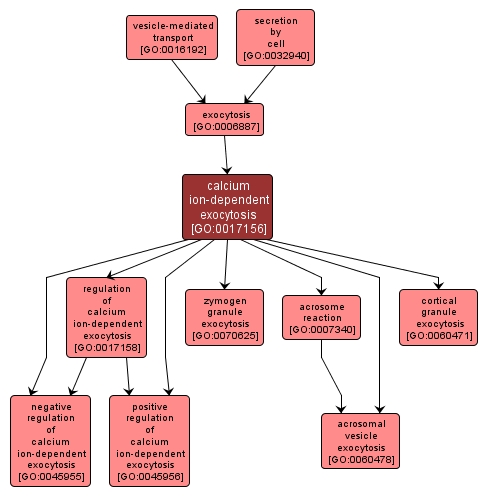
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
calcium ion-dependent exocytosis |
| Acc: |
GO:0017156 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The release of intracellular molecules (e.g. hormones, matrix proteins) contained within a membrane-bounded vesicle by fusion of the vesicle with the plasma membrane of a cell, requiring the presence of calcium ions. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|