GO TERM SUMMARY
|
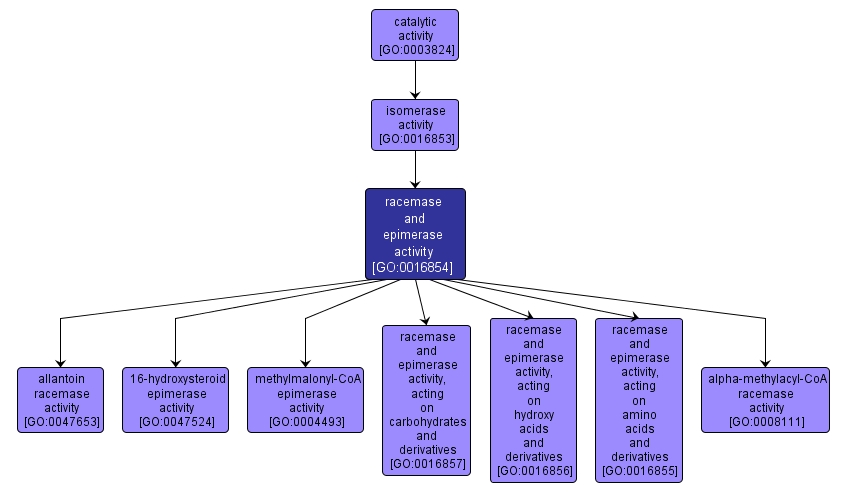
| Name: |
racemase and epimerase activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0016854 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of a reaction that alters the configuration of one or more chiral centers in a molecule. |
Synonyms:
- racemase and epimerase activity, acting on other compounds
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|