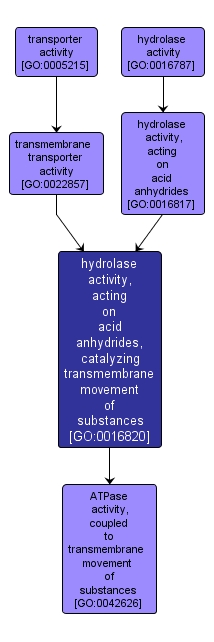
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides, catalyzing transmembrane movement of substances |
| Acc: |
GO:0016820 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of an acid anhydride to directly drive the transport of a substance across a membrane. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|