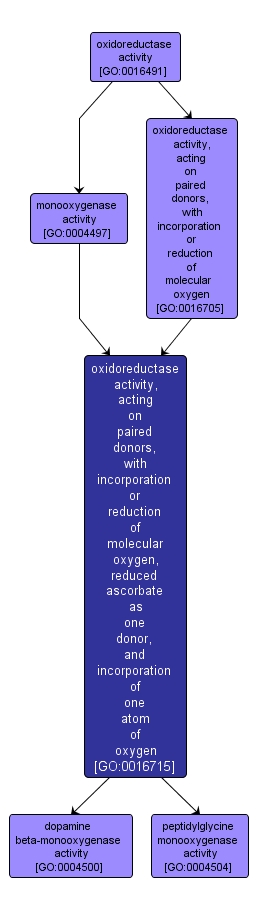
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
oxidoreductase activity, acting on paired donors, with incorporation or reduction of molecular oxygen, reduced ascorbate as one donor, and incorporation of one atom of oxygen |
| Acc: |
GO:0016715 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which hydrogen or electrons are transferred from reduced ascorbate and one other donor, and one atom of oxygen is incorporated into one donor. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|