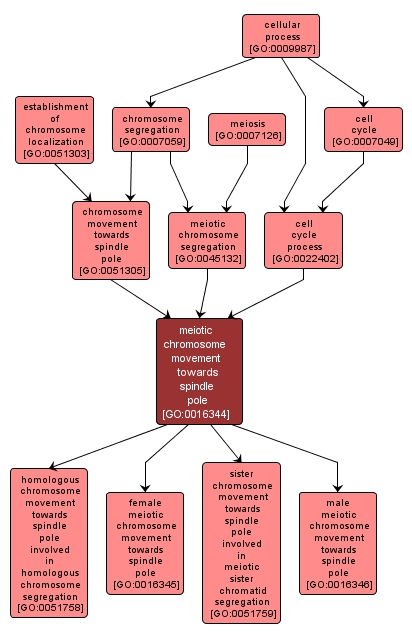
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
meiotic chromosome movement towards spindle pole |
| Acc: |
GO:0016344 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The cell cycle process whereby the directed movement of chromosomes from the center of the spindle towards the spindle poles takes place, mediated by the shortening of microtubules attached to the chromosomes. This occurs during meiosis. |
Synonyms:
- meiotic chromosome movement to spindle pole
- chromosome movement towards spindle pole during meiosis
- chromosome migration to spindle pole during meiosis
- meiotic chromosome movement
|