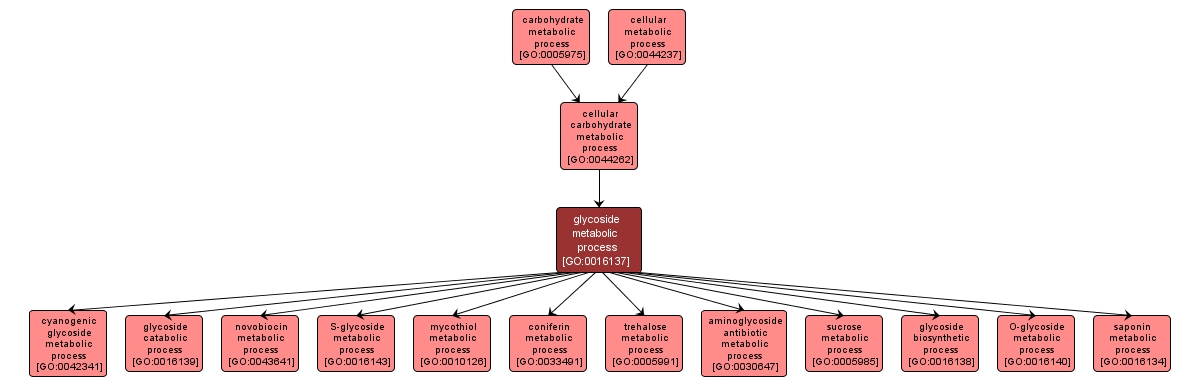
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
glycoside metabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0016137 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways involving glycosides, compounds in which a glycosyl group is substituted into a hydroxyl, thiol or selenol group in another compound. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|