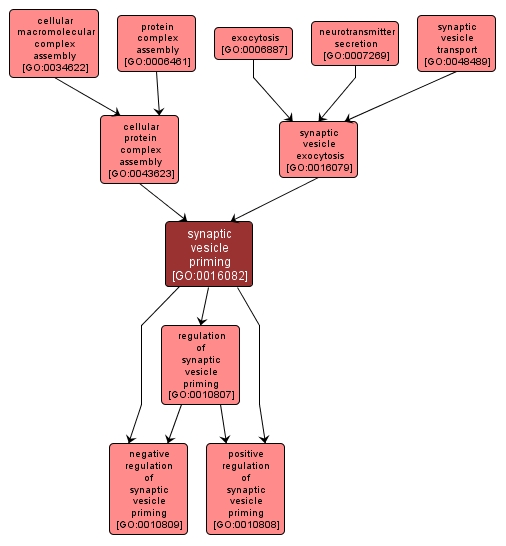
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
synaptic vesicle priming |
| Acc: |
GO:0016082 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The formation of SNARE-containing complexes, bringing synaptic vesicle membrane and plasma membranes into close proximity and thereby facilitating membrane fusion. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|