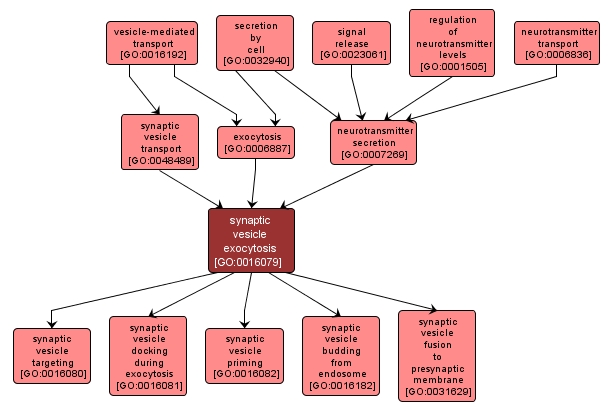
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
synaptic vesicle exocytosis |
| Acc: |
GO:0016079 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Fusion of intracellular membrane-bounded vesicles with the pre-synaptic membrane of the neuronal cell resulting in release of neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|