GO TERM SUMMARY
|
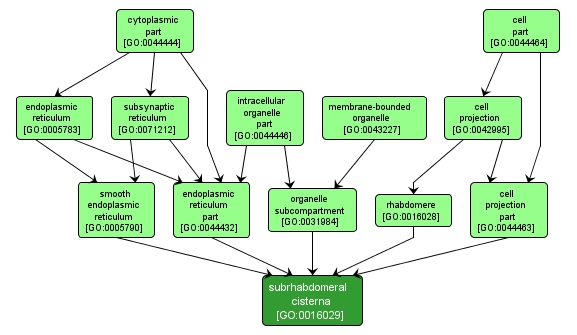
| Name: |
subrhabdomeral cisterna |
| Acc: |
GO:0016029 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
A membrane-bounded compartment that is found at the base of the rhabdomere and contains stored calcium, InsP3 receptors and smooth endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. |
Synonyms:
- submicrovillar cisterna
- SMC
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|