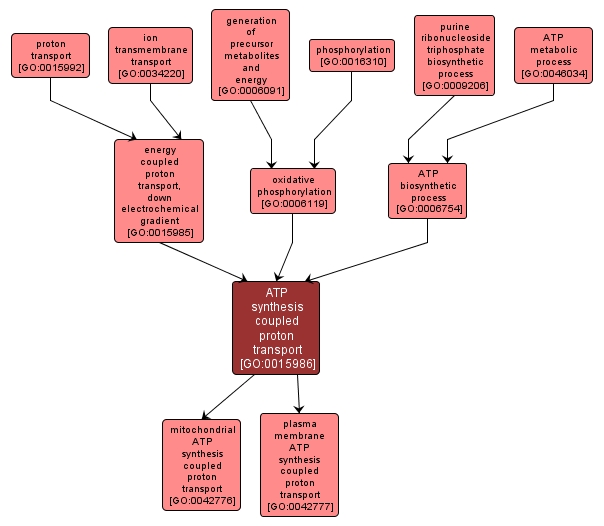
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
ATP synthesis coupled proton transport |
| Acc: |
GO:0015986 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The transport of protons across a membrane to generate an electrochemical gradient (proton-motive force) that powers ATP synthesis. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|