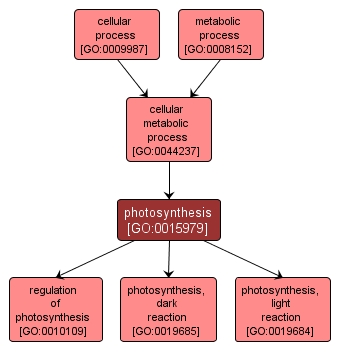
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
photosynthesis |
| Acc: |
GO:0015979 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The synthesis by organisms of organic chemical compounds, especially carbohydrates, from carbon dioxide (CO2) using energy obtained from light rather than from the oxidation of chemical compounds. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|