GO TERM SUMMARY
|
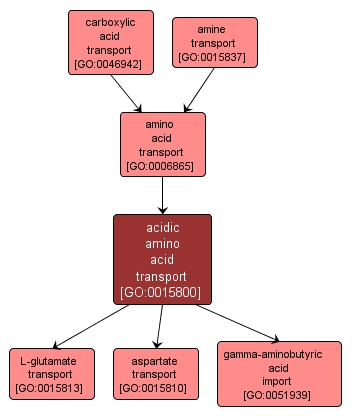
| Name: |
acidic amino acid transport |
| Acc: |
GO:0015800 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The directed movement of acidic amino acids, amino acids with a pH below 7, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|