GO TERM SUMMARY
|
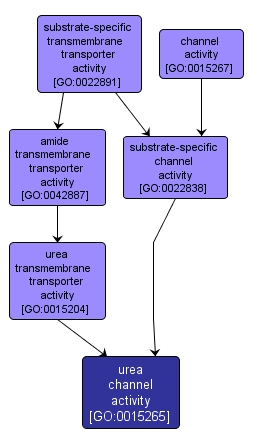
| Name: |
urea channel activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0015265 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of urea (by an energy-independent process) involving passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|