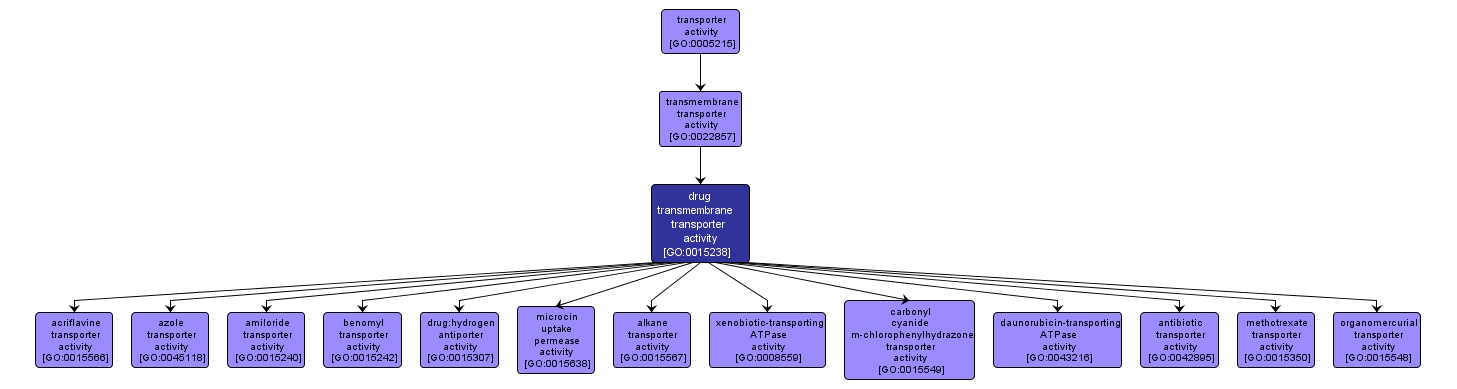
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
drug transmembrane transporter activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0015238 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Enables the directed movement of a drug from one side of a membrane to the other. A drug is any naturally occurring or synthetic substance, other than a nutrient, that, when administered or applied to an organism, affects the structure or functioning of the organism; in particular, any such substance used in the diagnosis, prevention, or treatment of disease. |
Synonyms:
- GO:0015564
- multidrug transporter activity
- multidrug efflux pump activity
- GO:0015559
- GO:0015239
- multidrug, alkane resistant pump activity
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|