| Desc: |
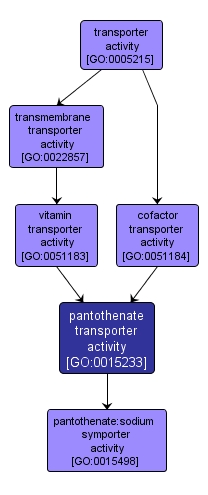
Enables the directed movement of pantothenate into, out of, within or between cells. Pantothenate is the anion of pantothenic acid, the amide of beta-alanine and pantoic acid; it is a B complex vitamin that is a constituent of coenzyme A and is distributed ubiquitously in foods. |