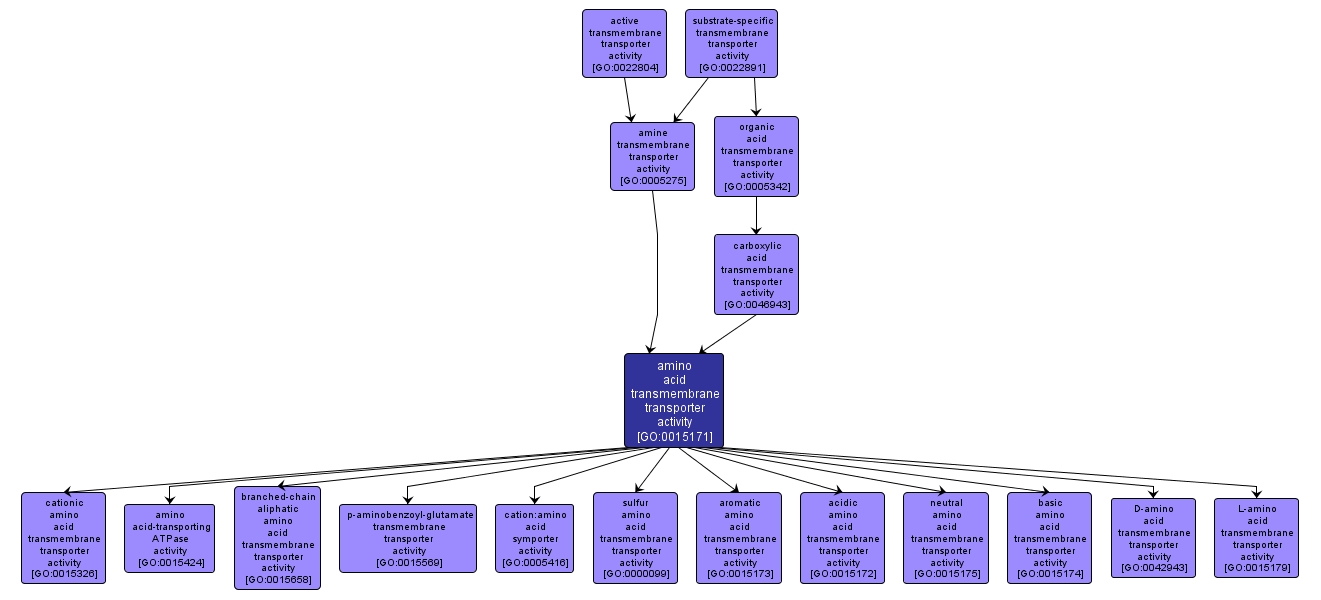
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
amino acid transmembrane transporter activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0015171 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the transfer of amino acids from one side of a membrane to the other. Amino acids are organic molecules that contain an amino group and a carboxyl group. |
Synonyms:
- general amino acid permease activity
- amino acid/choline transmembrane transporter activity
- hydroxy/aromatic amino acid permease activity
- amino acid transporter activity
- amino acid permease activity
- GO:0015359
|