GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
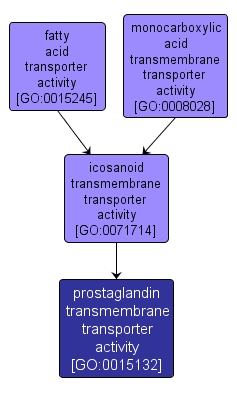
prostaglandin transmembrane transporter activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0015132 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the transfer of prostaglandins from one side of the membrane to the other. A prostaglandin is any of a group of biologically active metabolites which contain a cyclopentane ring due to the formation of a bond between two carbons of a fatty acid. They have a wide range of biological activities. |
Synonyms:
- prostaglandin/thromboxane transporter activity
|