GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
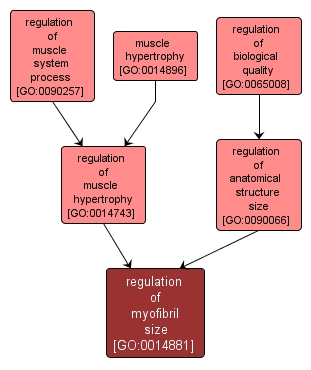
regulation of myofibril size |
| Acc: |
GO:0014881 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that modulates the size of myofibrils. A myofibril is the contractile element of skeletal and cardiac muscle. It is a long, highly organized bundle of actin, myosin, and other proteins that contracts by a sliding filament mechanism. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|