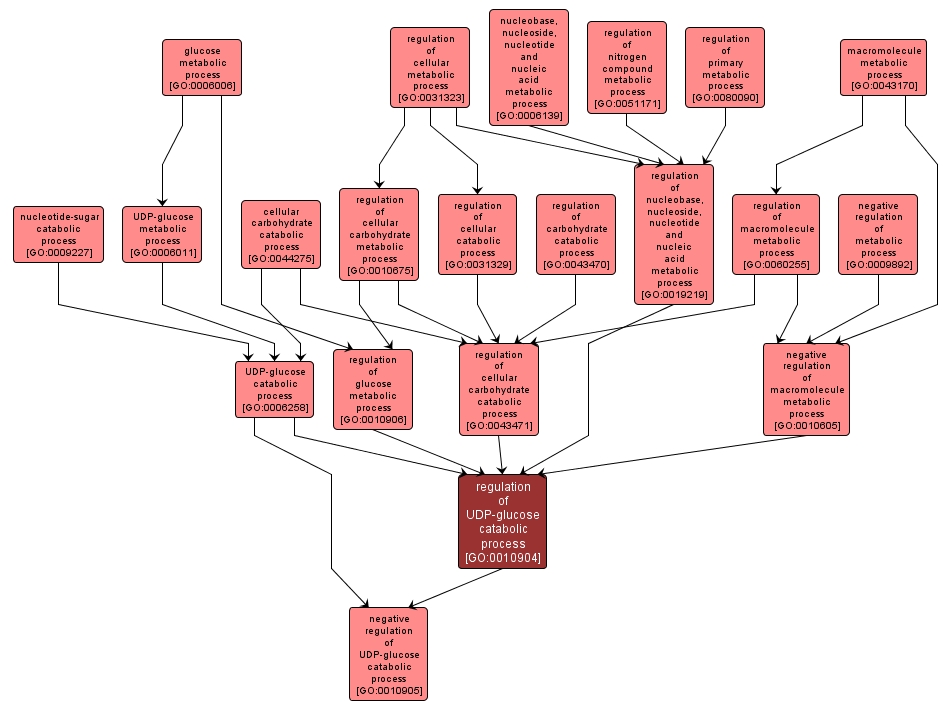
| Desc: |
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of UDP-glucose catabolism. UDP-glucose catabolic processes are the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of UDP-glucose, uridinediphosphoglucose, a substance composed of glucose in glycosidic linkage with uridine diphosphate. |