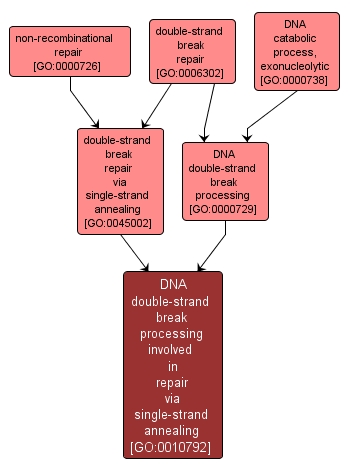
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
DNA double-strand break processing involved in repair via single-strand annealing |
| Acc: |
GO:0010792 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The 5' to 3' exonucleolytic resection of the DNA at the site of the break to form a 3' single-strand DNA overhang that results in the repair of a double strand break via single-strand annealing. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|