GO TERM SUMMARY
|
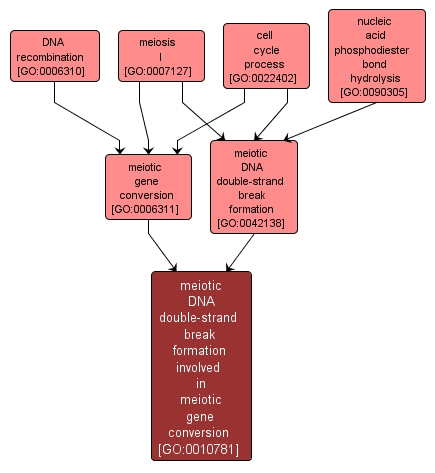
| Name: |
meiotic DNA double-strand break formation involved in meiotic gene conversion |
| Acc: |
GO:0010781 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The cell cycle process whereby double-strand breaks are generated at defined hotspots throughout the genome during meiosis I resulting in meiotic gene conversion. Meiotic gene conversion is the cell cycle process whereby genetic information is transferred from one helix to another. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|