| Desc: |
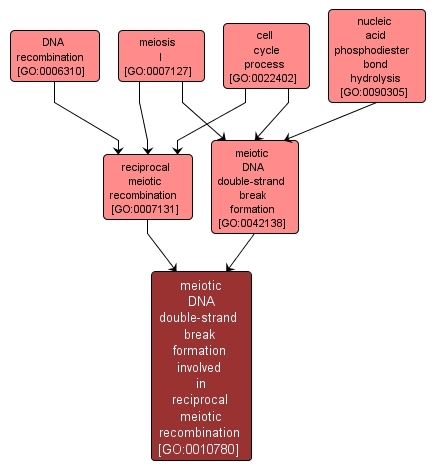
The cell cycle process whereby double-strand breaks are generated at defined hotspots throughout the genome during meiosis I resulting in meiotic recombination. Meiotic recombination is the cell cycle process whereby double strand breaks are formed and repaired through a double Holliday junction intermediate. |