GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
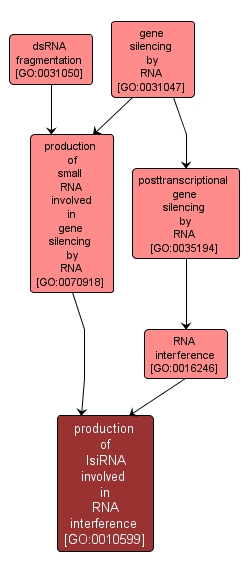
production of lsiRNA involved in RNA interference |
| Acc: |
GO:0010599 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Cleavage of double-stranded RNA to form lsiRNA (long small interfering RNA), a class of siRNAs 30 to 40 nt in length. lsiRNAs are induced by pathogen infection or under specific growth conditions. |
Synonyms:
- RNA interference, production of lsiRNA
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|