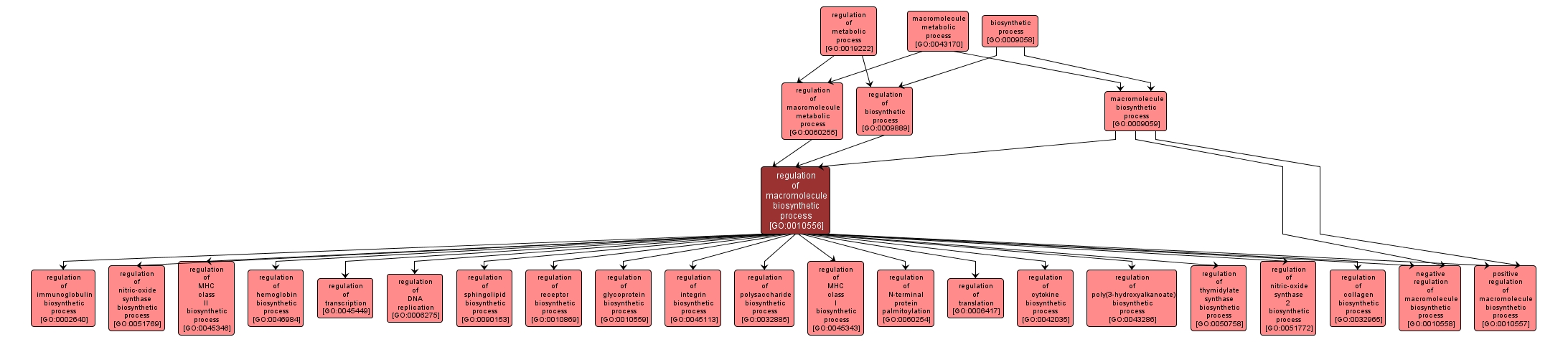
| Desc: |
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass. |