GO TERM SUMMARY
|
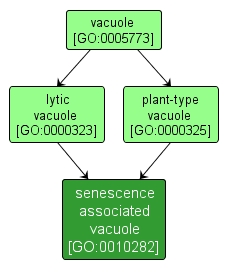
| Name: |
senescence associated vacuole |
| Acc: |
GO:0010282 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
A lytic vacuole that is maintained at acidic pH and has different tonoplast composition compared to the central vacuole. Found during leaf senescence and develops in the peripheral cytoplasm of cells that contain chloroplast. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|