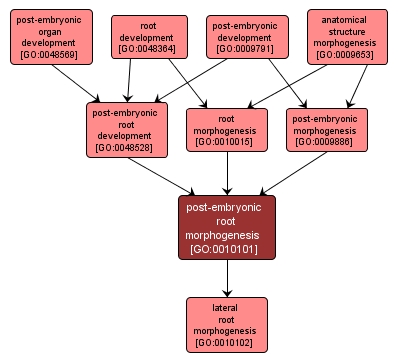
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
post-embryonic root morphogenesis |
| Acc: |
GO:0010101 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process by which the anatomical structures of the post-embryonic root are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. The post-embryonic root is the root formed after the embryonic phase has been completed. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|