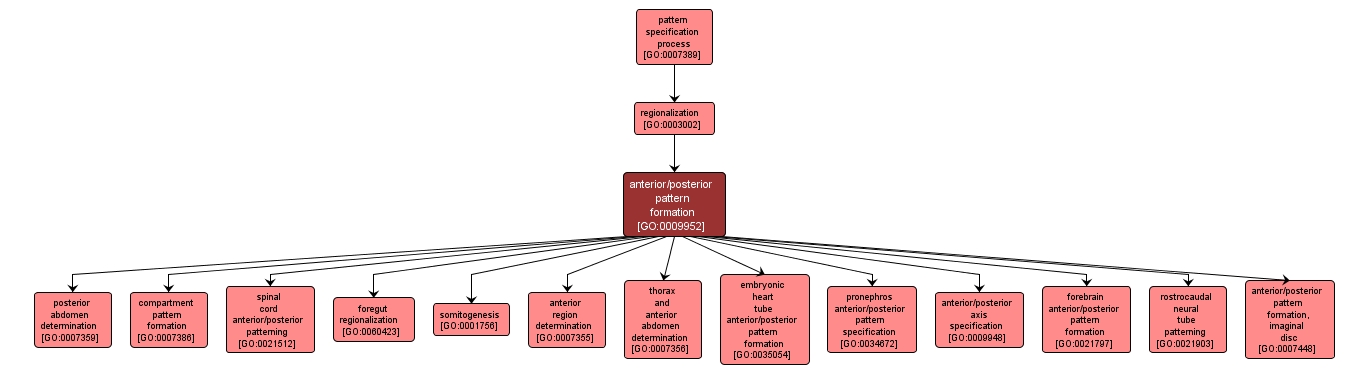
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
anterior/posterior pattern formation |
| Acc: |
GO:0009952 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The regionalization process by which specific areas of cell differentiation are determined along the anterior-posterior axis. The anterior-posterior axis is defined by a line that runs from the head or mouth of an organism to the tail or opposite end of the organism. |
Synonyms:
- anterior/posterior pattern specification
|