| Desc: |
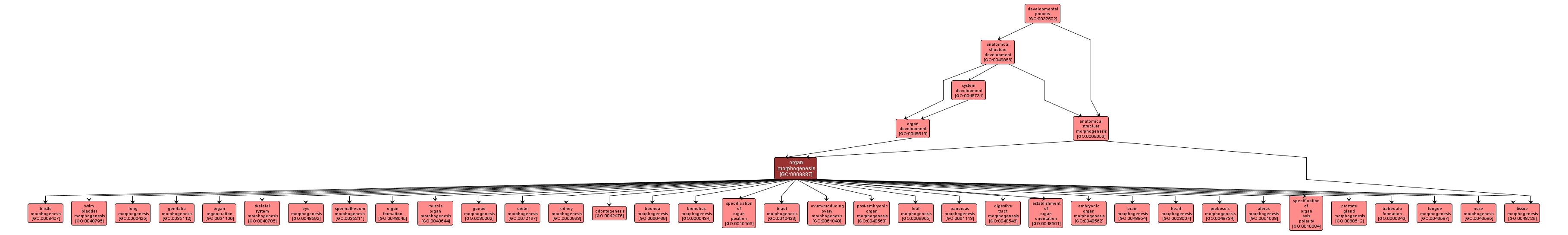
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions. |