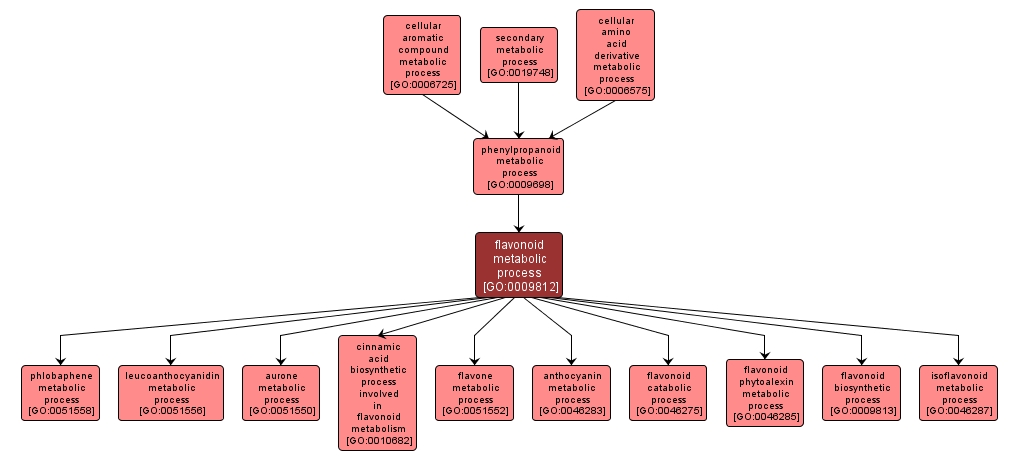
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
flavonoid metabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0009812 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways involving flavonoids, a group of water-soluble phenolic derivatives containing a flavan skeleton including flavones, flavonols and flavanoids, and anthocyanins. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|