| Desc: |
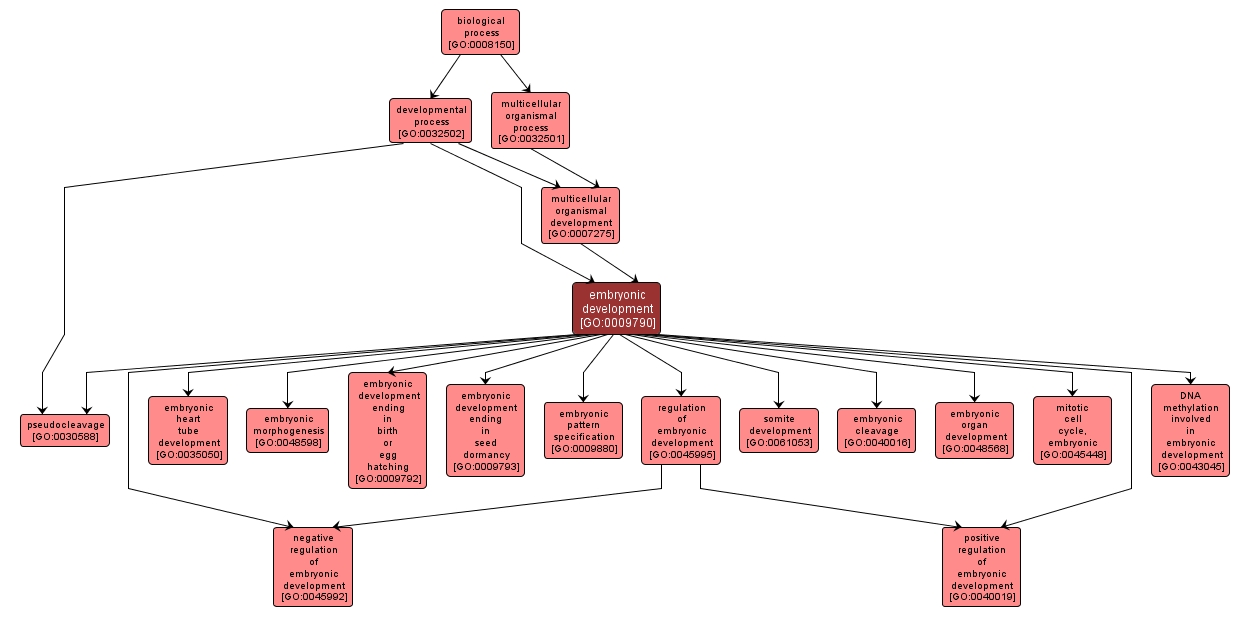
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an embryo from its formation until the end of its embryonic life stage. The end of the embryonic stage is organism-specific. For example, for mammals, the process would begin with zygote formation and end with birth. For insects, the process would begin at zygote formation and end with larval hatching. For plant zygotic embryos, this would be from zygote formation to the end of seed dormancy. For plant vegetative embryos, this would be from the initial determination of the cell or group of cells to form an embryo until the point when the embryo becomes independent of the parent plant. |