GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
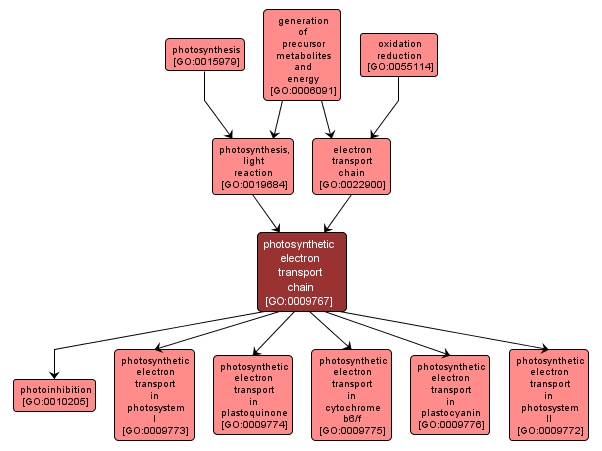
photosynthetic electron transport chain |
| Acc: |
GO:0009767 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
A process, occurring as part of photosynthesis, whereby light provides the energy for a series of electron carriers to operate together to transfer electrons and generate a transmembrane electrochemical gradient. |
Synonyms:
- electron carrier, chlorophyll electron transport system
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|