GO TERM SUMMARY
|
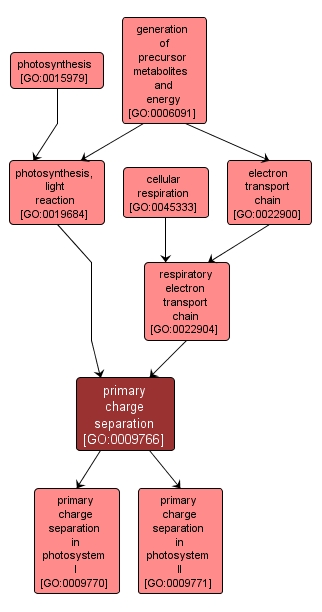
| Name: |
primary charge separation |
| Acc: |
GO:0009766 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
In the photosynthetic reaction centers, primary charge separation is initiated by the excitation of a molecule followed by the transfer of an electron to an electron acceptor molecule following energy transfer from light harvesting complexes. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|