GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
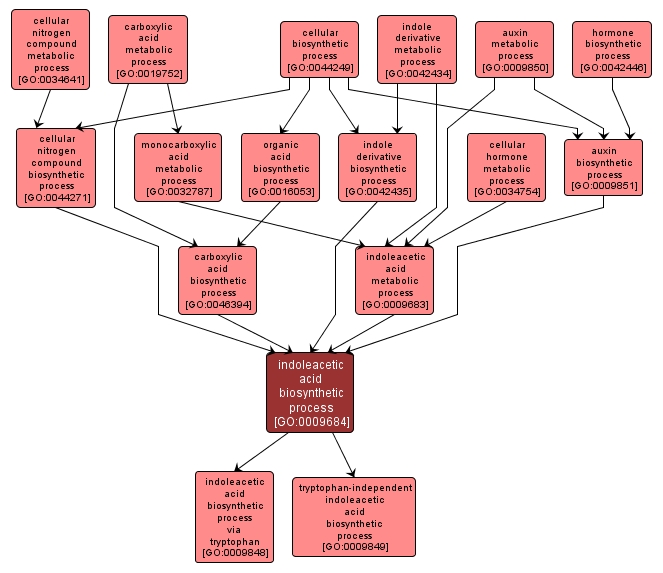
indoleacetic acid biosynthetic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0009684 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of indole-3-acetic acid, a compound which functions as a growth regulator in plants. |
Synonyms:
- indole acetic acid biosynthetic process
- indole-acetic acid biosynthesis
- IAA biosynthetic process
- indoleacetic acid anabolism
- indoleacetic acid formation
- indole acetic acid biosynthesis
- indole-acetic acid biosynthetic process
- indole-3-acetate biosynthesis
- indole-3-acetate biosynthetic process
- indoleacetic acid synthesis
- indoleacetic acid biosynthesis
|