GO TERM SUMMARY
|
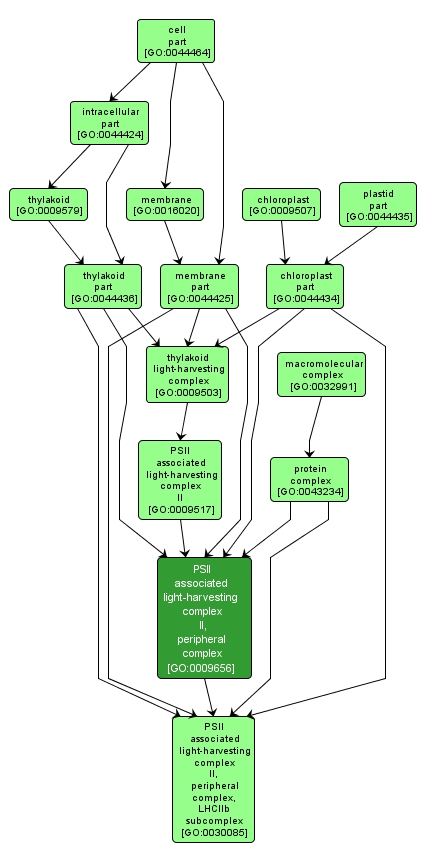
| Name: |
PSII associated light-harvesting complex II, peripheral complex |
| Acc: |
GO:0009656 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
Pigment-protein complex primarily associated to PSII in plants, green algae and cyanobacteria. Involved in state transitions that cause migration to PSI under certain environmental conditions such as high light. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|