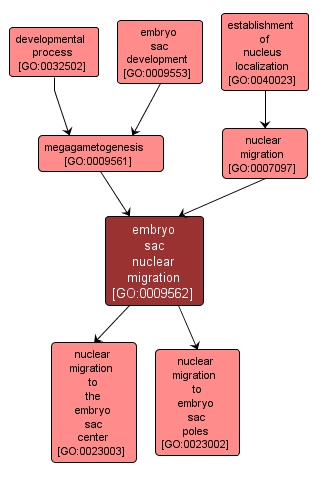
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
embryo sac nuclear migration |
| Acc: |
GO:0009562 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The directed movement of an embryo sac nucleus to the pole or center of the cell. |
Synonyms:
- female gametophyte nuclear migration
- megagametophyte nucleus migration
- megagametophyte nuclear migration
- embryo sac nucleus migration
- female gametophyte nucleus migration
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|