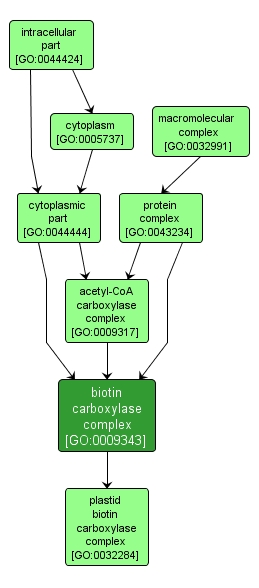
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
biotin carboxylase complex |
| Acc: |
GO:0009343 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
An enzyme complex that catalyzes the formation of carboxybiotin-carboxyl-carrier protein from biotin-carboxyl-carrier protein and carbon dioxide (CO2). |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|