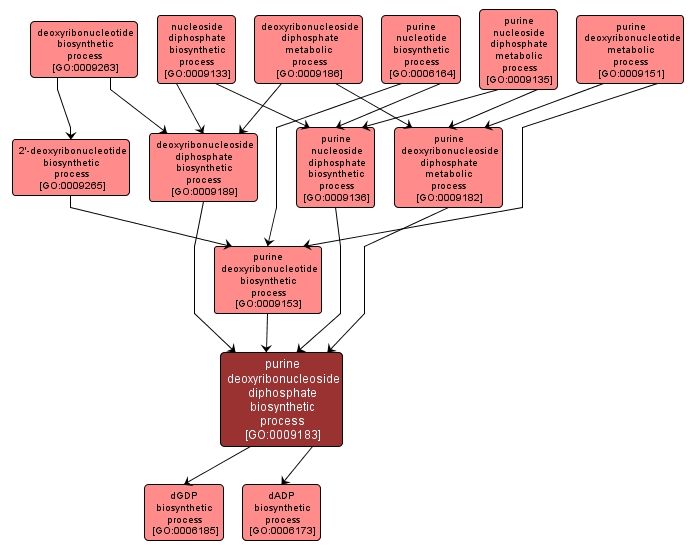
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
purine deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate biosynthetic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0009183 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of purine deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate, a glycosamine consisting of a purine base linked to a deoxyribose sugar esterified with diphosphate on its glycose moiety. |
Synonyms:
- purine deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate synthesis
- purine deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate formation
- purine deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate anabolism
- purine deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate biosynthesis
|