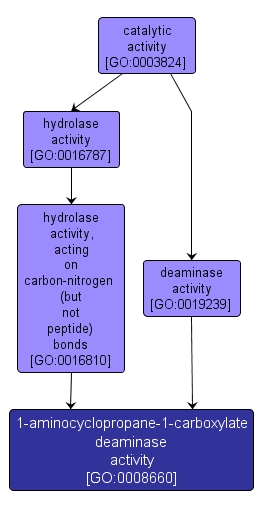
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0008660 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the reaction: 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate + H2O = 2-oxobutanoate + NH3. |
Synonyms:
- 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate endolyase (deaminating) activity
- GO:0018806
- 1-aminocyclopropane carboxylic acid deaminase activity
- 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate aminohydrolase (isomerizing)
- ACC deaminase activity
|