GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
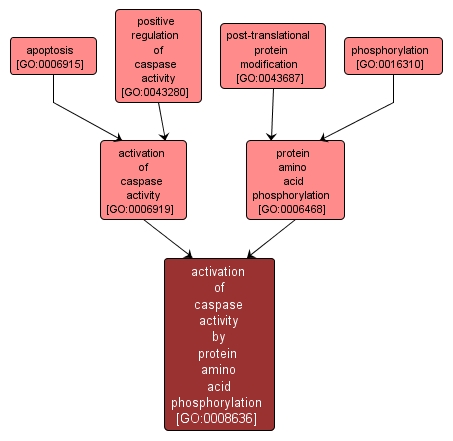
activation of caspase activity by protein amino acid phosphorylation |
| Acc: |
GO:0008636 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Upregulation of the activity of a caspase, any of a group of cysteine proteases involved in apoptosis, by the addition of a phosphate group. |
Synonyms:
- caspase activation via phosphorylation
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|