GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
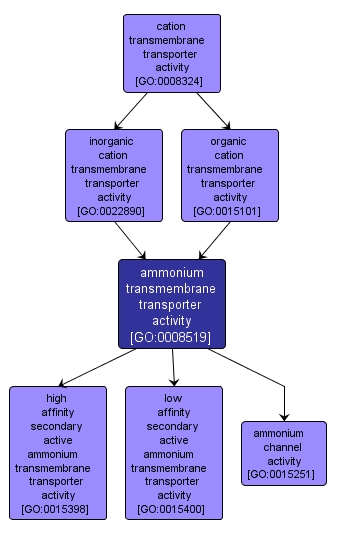
ammonium transmembrane transporter activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0008519 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the transfer of ammonium from one side of a membrane to the other. Ammonium is the cation NH4+ which is formed from N2 by root-nodule bacteria in leguminous plants and is an excretory product in ammonotelic animals. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|