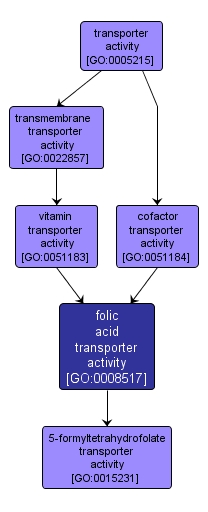
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
folic acid transporter activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0008517 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Enables the directed movement of folic acid (pteroylglutamic acid) into, out of, within or between cells. Folic acid is widely distributed as a member of the vitamin B complex and is essential for the synthesis of purine and pyrimidines. |
Synonyms:
- vitamin B9 transporter activity
- folate transporter activity
- vitamin M transporter activity
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|