GO TERM SUMMARY
|
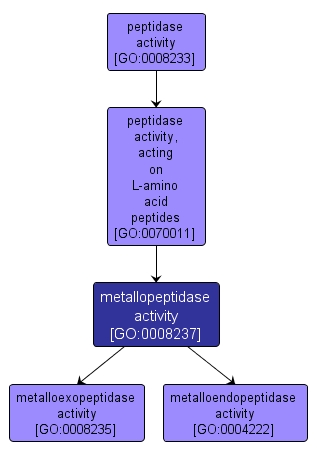
| Name: |
metallopeptidase activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0008237 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of peptide bonds by a mechanism in which water acts as a nucleophile, one or two metal ions hold the water molecule in place, and charged amino acid side chains are ligands for the metal ions. |
Synonyms:
- metalloprotease activity
- metalloproteinase activity
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|