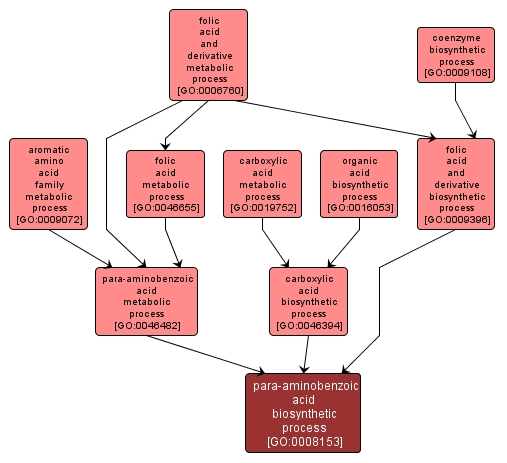
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of para-aminobenzoic acid, an intermediate in the synthesis of folic acid, a compound which some organisms, e.g. prokaryotes, eukaryotic microbes, and plants, can synthesize de novo. Others, notably mammals, cannot. In yeast, it is present as a factor in the B complex of vitamins. |