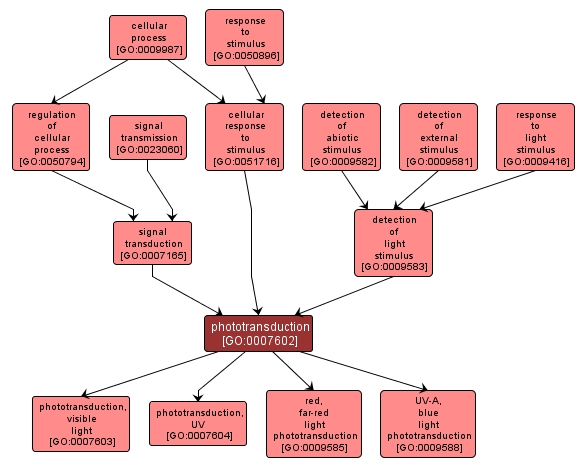
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
phototransduction |
| Acc: |
GO:0007602 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The sequence of reactions within a cell required to convert absorbed photons into a molecular signal. |
Synonyms:
- phototrophin mediated phototransduction
- opsin
- phototransduction, visible light, light adaptation
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|