GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
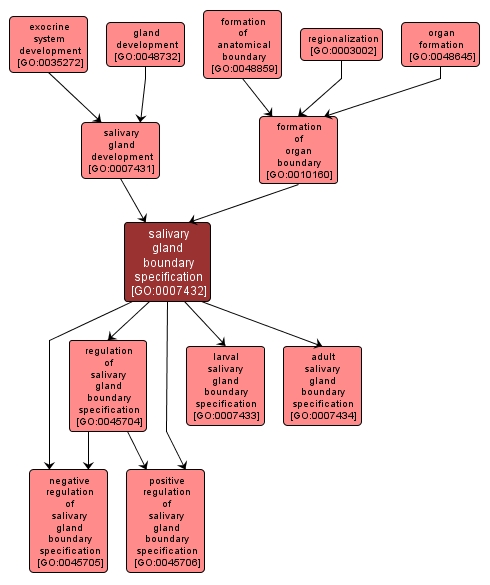
salivary gland boundary specification |
| Acc: |
GO:0007432 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Determination of where the salivary gland forms, the total number of salivary gland cells and how many cells are allocated to each of the specialised cell types within the salivary gland. |
Synonyms:
- salivary gland determination
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|