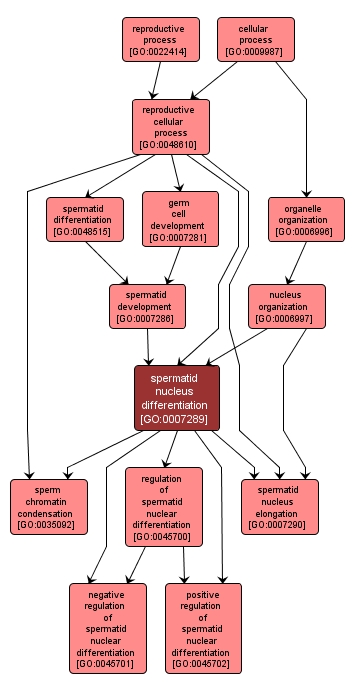
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
spermatid nucleus differentiation |
| Acc: |
GO:0007289 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The specialization of the spermatid nucleus during the development of a spermatid into a mature male gamete competent for fertilization. |
Synonyms:
- spermatid nuclear differentiation
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|