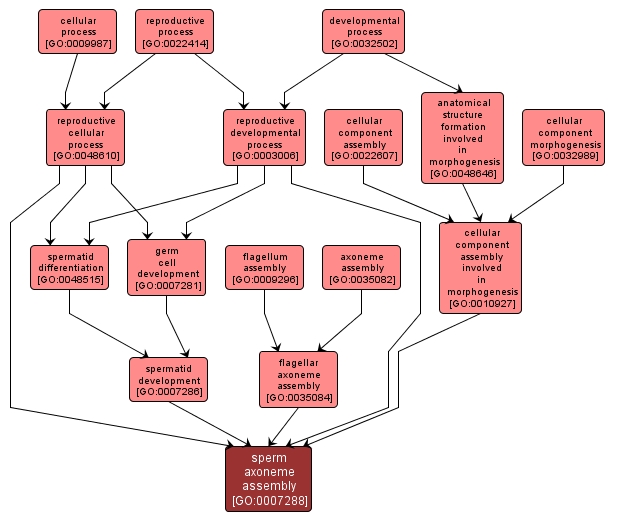
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
sperm axoneme assembly |
| Acc: |
GO:0007288 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The assembly and organization of the sperm flagellar axoneme, the bundle of microtubules and associated proteins that forms the core of the eukaryotic sperm flagellum, and is responsible for movement. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|